Testing plays a vital role in ensuring the quality and reliability of mobile apps. By thoroughly testing the software during the development process, mobile software developers can identify and address issues early, leading to a more stable and user-friendly application.
In this article, we will explore the results of a survey conducted among mobile software developers. We will delve into the reasons for writing tests and an overview of different test types.
📊 Survey Results
I conducted a survey of over 50 mobile developers to learn about their testing practices in their projects.
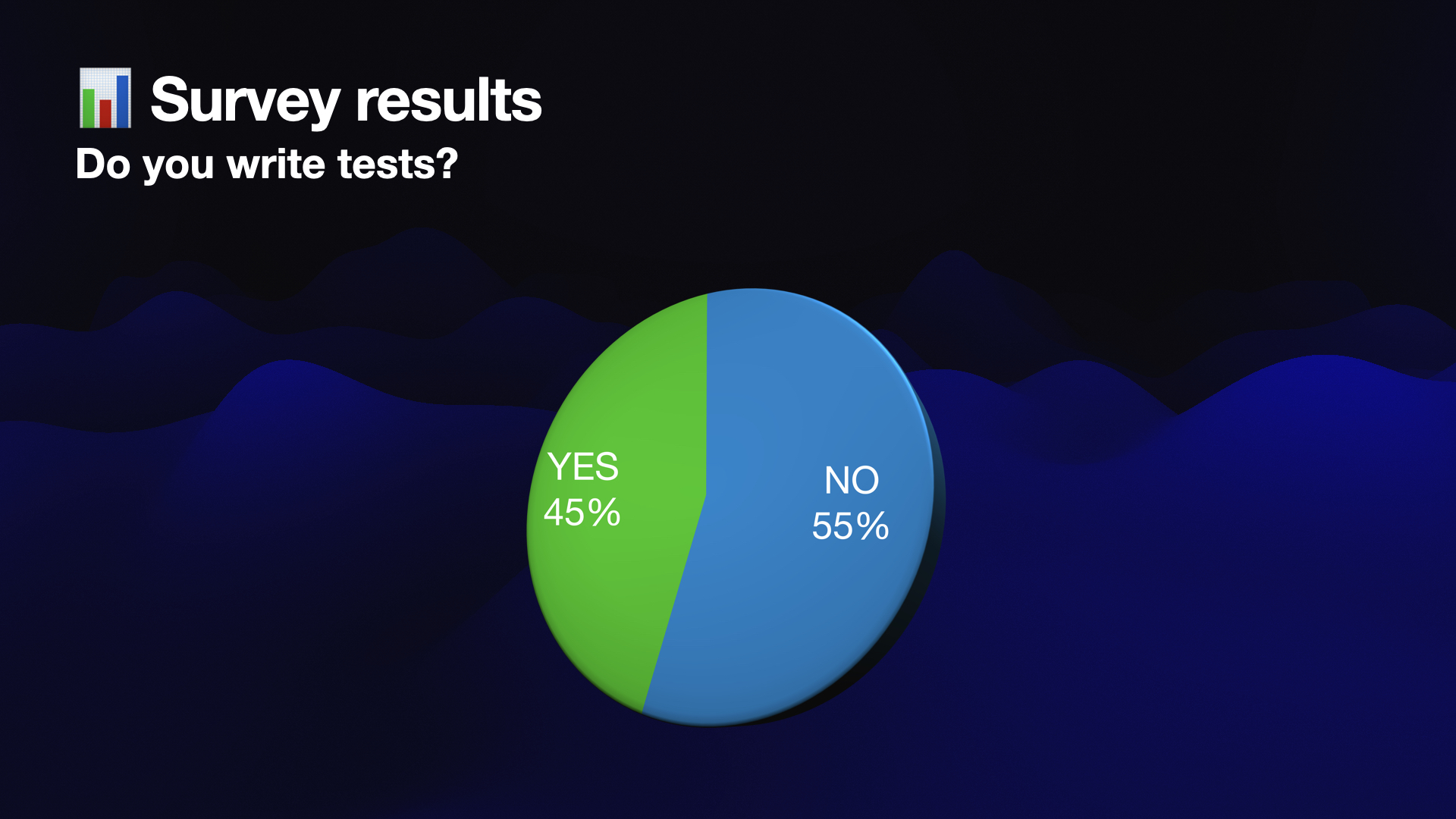 The results showed that 55% of the surveyed developers do not write tests, while the other 45% believed it is important.
The results showed that 55% of the surveyed developers do not write tests, while the other 45% believed it is important.
When asked why they do not write tests, the main reasons cited were:
- ⏰ Lack of sufficient time to dedicate to writing and maintaining tests.
- 👎 The perception that their current codebase is unsuitable for effective testing.
- 🔃 Frequent code changes that make maintaining tests challenging.
- ❌ Limited proficiency in writing comprehensive tests.
- 🤖 Overreliance on end-to-end testing as a substitute for more granular testing practices.
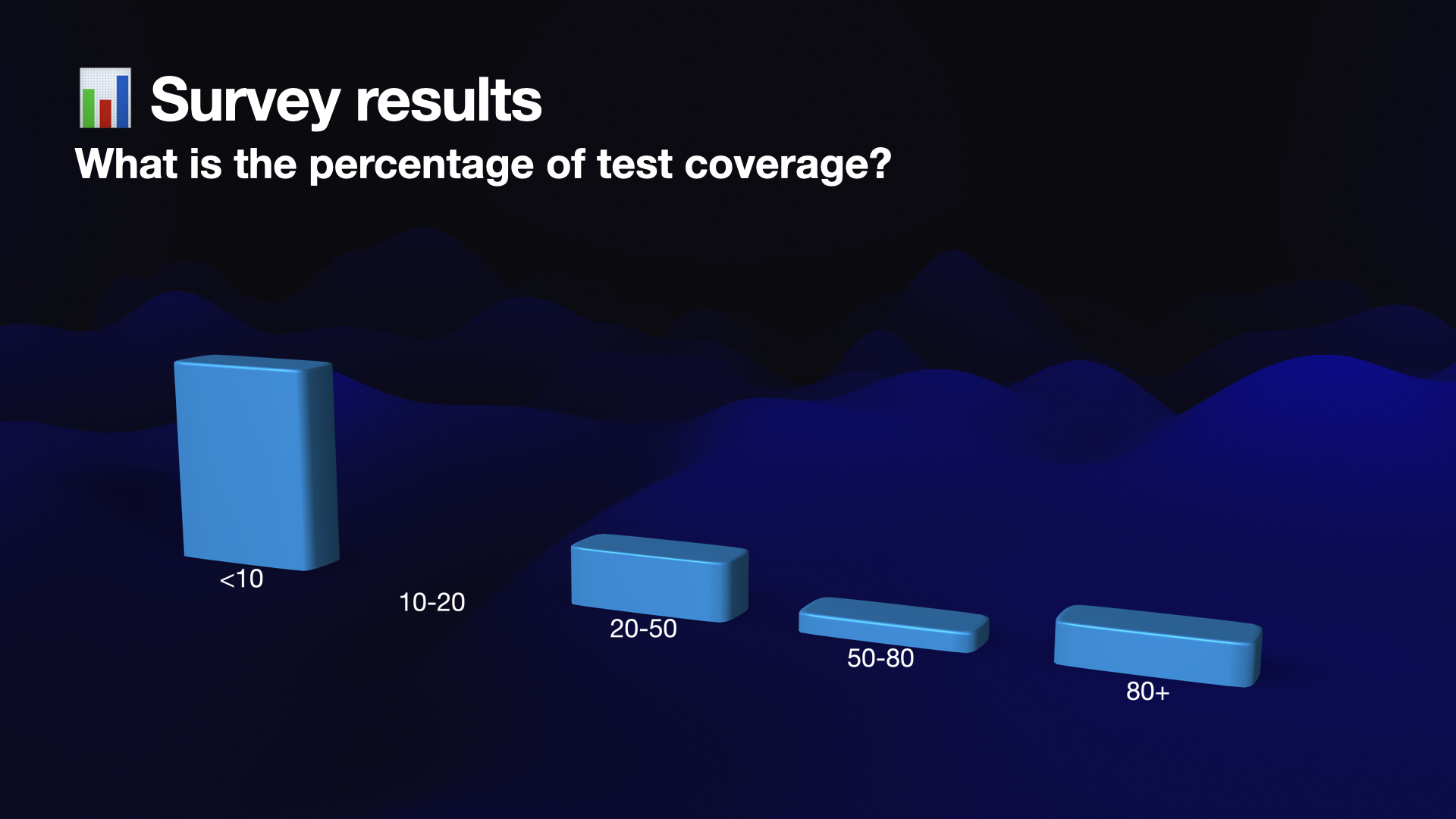 The second question in the survey focused on code coverage, revealing that a significant number of developers had low code coverage, with only a few achieving coverage above 80%. In fact, the majority of respondents had a code coverage level of merely 10%.
The second question in the survey focused on code coverage, revealing that a significant number of developers had low code coverage, with only a few achieving coverage above 80%. In fact, the majority of respondents had a code coverage level of merely 10%.
To further explore this aspect, I posed additional questions to developers with less than 10% code coverage and those with more than 80% code coverage. For developers with less than 10% coverage, I asked: What areas do you cover in testing? Their responses shed light on the following:
- Critical functionality: These developers prioritize testing critical functionalities of the app, such as onboarding processes and payment systems. These components are crucial for ensuring a seamless user experience and require thorough validation.
- Difficult logic: Testing efforts extend to challenging and complex logic areas of the codebase, including parsers, calculations, algorithms, and other intricate components that significantly contribute to the app’s functionality.
- Business logic: Developers also focus on testing the business logic of the app, encompassing view models and use cases. These components represent the core functionalities and workflows of the application.
Conversely, developers with more than 80% code coverage were asked about the areas they do not cover. Their responses included the following:
- Humble Objects: These developers mentioned that they do not write tests specifically for Humble Objects, which are minimalistic and decoupled classes popularized by Uncle Bob (Robert C. Martin) in his book. Humble Objects handle low-level details and interactions and are isolated from the complexities of the system.
- A/B tests: Another area not covered by these developers is A/B tests. Due to the potential for frequent changes, they opt not to write tests for this functionality, as it may undergo modifications in the near future.
Based on these two answers, we can determine which areas to prioritize for test coverage in the absence of tests in our app and establish criteria for when to conclude our testing efforts.
🤔 Reasons to Write Tests
 Just like road markings guide drivers and enhance safety, tests provide several benefits in software development. Let’s explore the parallels between road markings and testing, highlighting their shared pros.
Just like road markings guide drivers and enhance safety, tests provide several benefits in software development. Let’s explore the parallels between road markings and testing, highlighting their shared pros.
- Increased Safety and Reduced Chances of Crashes: Road markings serve as visual cues that guide drivers, enhancing road safety and reducing the likelihood of accidents. Similarly, testing in software development minimizes the chances of errors or bugs, ensuring a stable and secure product. By thoroughly testing software, developers can identify and rectify potential issues, leading to a more robust and reliable application.
- Easy Adaptation for Drivers in New Roads: Road markings provide valuable information to drivers, especially when navigating unfamiliar roads. They offer clear guidance and help drivers adapt quickly to new surroundings. In a similar vein, tests in software development contribute to the smooth onboarding process for new team members. Well-written tests serve as documentation and examples, allowing new developers to understand the existing codebase more efficiently and make necessary modifications confidently.
- Limitations that Help Drivers Ride Without Stress: Road markings set boundaries and provide clear instructions, helping drivers navigate complex situations and reduce stress on the road. Similarly, testing imposes limitations on the code-writing process, promoting better coding practices and improved code quality. Tests serve as checks and balances, ensuring that developers adhere to coding standards, maintain consistency, and produce reliable software.
In summary, testing shares key advantages with road markings. It reduces the chances of errors, facilitates the onboarding process for new team members, and establishes limitations that improve code quality. By embracing testing practices, software developers can mitigate risks, enhance productivity, and deliver robust and reliable applications, just as road markings contribute to safer and more efficient roadways.
Other Benefits of Tests:
Writing tests brings several benefits to mobile software development:
- 🏎️ Development speed: Tests catch errors early, allowing developers to fix problems promptly and maintain a faster development pace.
- ✅ Safe refactoring: Tests act as a safety net during code refactoring, ensuring that changes do not introduce regressions or unintended consequences.
- 🐞 Early detection of bugs: Tests help identify issues and unexpected behavior early in the development cycle, enabling developers to address them promptly and reduce debugging efforts later on.
- 📈 Better code quality: Writing tests encourages cleaner and more maintainable code, leading to improved overall code quality.
- 🙌 Reduced manual testing: Automated tests eliminate the need for extensive manual testing, saving time and effort while maintaining consistent and reliable results.
🎛️ Test Types Overview
Testing in software development can be categorized into three types, represented by a pyramid 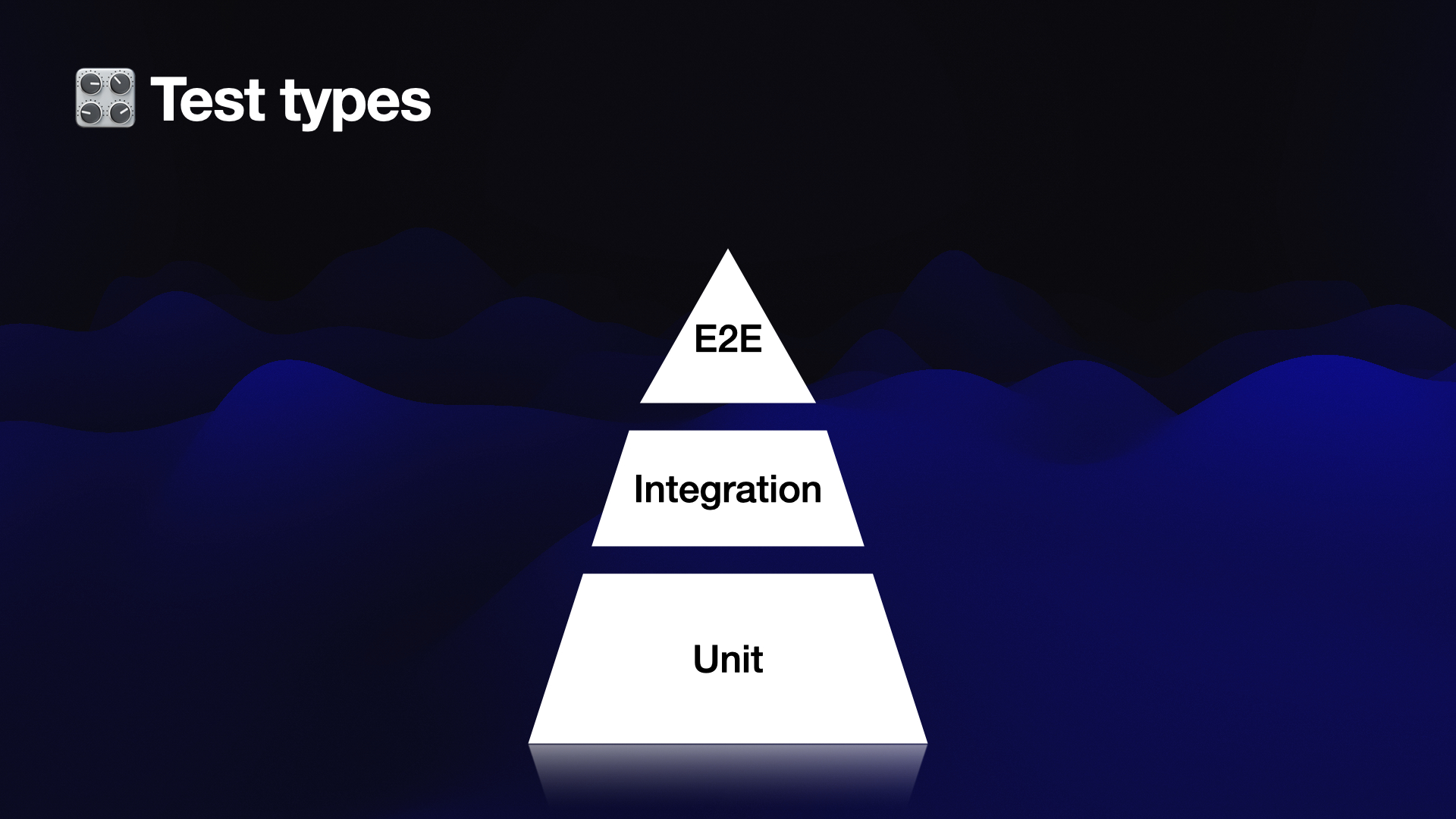
- Unit Testing: Unit testing, comparable to testing individual components of a rocket like the fuel tank or combustion chamber, focuses on testing isolated units of code. It verifies that each unit performs correctly in isolation, catching bugs early on. Unit testing is efficient and cost-effective.
- Integration Testing: Similar to verifying the interaction between the fuel tank and combustion chamber, integration testing ensures that different components work together properly. It validates the communication and collaboration between units that have passed their individual tests.
- End-to-End Testing: End-to-end testing, analogous to launching a rocket to observe its behavior throughout the entire process, validates the entire system as a whole. It simulates real-life scenarios, including user interactions, and ensures seamless functionality across all components. End-to-end testing represents the highest level of testing and is comprehensive but can be more expensive to maintain.
In summary, unit testing focuses on testing isolated units, integration testing verifies component interactions, and end-to-end testing validates the system as a whole, mirroring the stages of a rocket’s development and launch process. While the traditional testing pyramid emphasizes a larger base of unit tests and fewer end-to-end tests, some teams prioritize end-to-end testing more prominently. This approach, known as the inverted pyramid, ensures thorough validation of features before releasing them to end users. 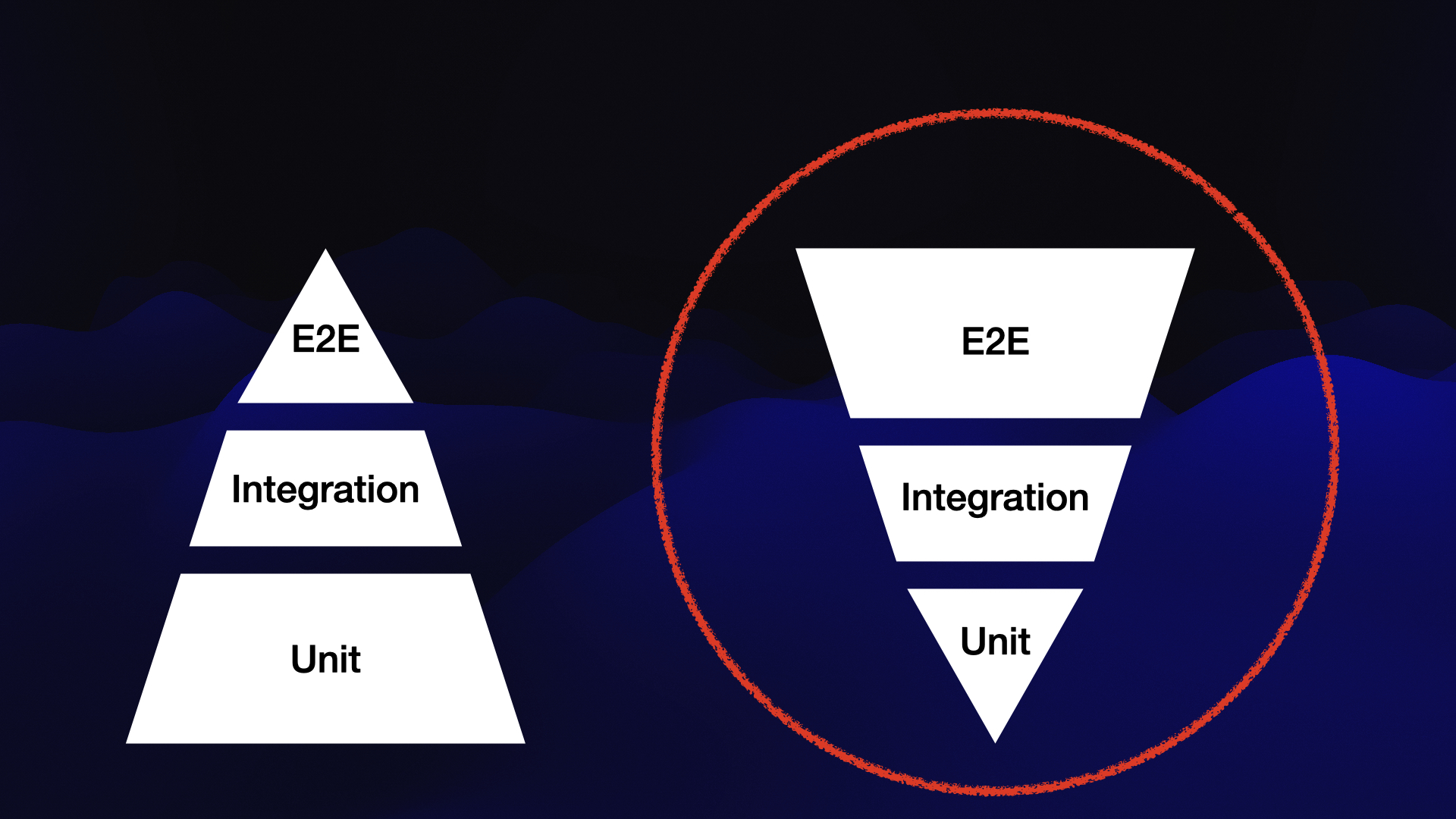 In my team, we prefer this type of pyramid. However, it is worth noting that the majority of mobile development teams typically adhere to the standard testing pyramid.
In my team, we prefer this type of pyramid. However, it is worth noting that the majority of mobile development teams typically adhere to the standard testing pyramid. 
🎁 Bonus: Tools that we use in our team
It is essential to leverage the right tools to streamline and optimize the testing process. Here are a few tools which used by our team:
- Code Generation: Code generation tools, such as Sourcery, automate the creation of fake data and mocks, making the testing process more efficient and reducing manual effort.
- Snapshot Testing: Snapshot testing tools like Swift Snapshot Testing enable developers to capture screenshots of the user interface and compare them to previously saved snapshots. This technique helps identify unintended changes and ensures visual consistency across different app versions.
- Appium: Appium is an end-to-end testing tool that simulates user activities and verifies system behavior from a user’s perspective. It utilizes Espresso or UIAutomator2 for Android apps and XCUI for iOS apps. With a black box testing approach, Appium evaluates all relevant subsystems, including UI/UX, server, database, and dependencies.
- CI/CD Tools: Fastlane, Danger, and Xcov automate various tasks related to building, testing, and deploying mobile apps. Fastlane enables script execution, Danger integrates with the code review process for analysis, and Xcov assesses code coverage using changes from pull requests.
By incorporating these tools into your testing process, you can improve efficiency, code quality, and overall app reliability.
🎬 Conclusion
In the fast-paced world of mobile app development, testing holds the key to success. It provides confidence in app quality and stability, ensuring a seamless user experience. The survey results highlighted the importance of test-driven development and the challenges faced by mobile software developers. By incorporating different types of tests, such as unit testing, integration testing, and end-to-end testing, developers can enhance the reliability, maintainability, and overall quality of their mobile apps.
Testing is not a burden but an investment in creating successful mobile apps that stand out in the competitive market. By prioritizing testing and utilizing the right tools, you can deliver mobile apps that meet user expectations and drive business success.
